After years of stories of viruses, stolen personal
information & DOS (Denial of Service) attacks, it’s clear that security
is important for every application...in our discussion we'll describe
Windows Communication Foundation (WCF) security features and how to use them to
help secure messages..
What are the core security features that WCF
addresses?
There
are four core security features that WCF addresses:
1) Confidentiality: This feature ensures that information
does not go in to the wrong hands when it travels from the client to the server
or vica versa.
2) Integrity: This feature ensures that the
receiver of the message gets the same information that the sender sent without
any data tampering.
3) Authentication: This feature verifies who the sender
is and who the receiver is.
4) Authorization: This feature verifies whether the
user is authorized to perform the action they are requesting from the
application.
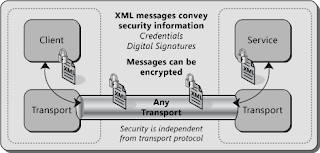
Security Infrastructure...
Let's
try to understand how security at Transport & Message Layer can prevent
unauthorized viewing and tampering with message when it travels from the client to the server or vica
versa. & Implementation of user level security: Authentication and
Authorization. In This Blog (Programming WCF Security - I). We will discuss Transport Level Security. Message Level Security ,Authentication and
Authorization we'll cover in next.
In
WCF, the secure transports available for use are HTTP, Transmission Control Protocol (TCP)& Microsoft Message Queuing ( MSMQ ). For a
transport to be secure, all communications that take place across the channel
must be encrypted, Contrast this with Message Level security, which would encrypt only message component of communication.
In WCF, much about transport layer security is automatically
handled or Abstracted to developers, We just have to implement some
configuration details then rest will be handheld by WCF itself. A
Number of benefits accrue by Transport layer security such as:
- Protection from sniffing network traffic , to obtain sensitive information
- Protection from Phishing attacks
- Protection from message alteration when it travels from the client to the server or vica versa.
- Protection from Reply attacks
Because Integrity is provided by ensuring that the
Encryption Key is shared between only the two parties involved in
communication. Privacy is guaranteed through the Encryption process,
Mutual authentication of sender and receiver is provided because the
credentials are encrypted as part of message...
Transport level security is directly related to the binding
we are using, with one exception BasicHttpBinding, all the
binding available for WCF include a default security mode... Even we can
configure BasicHttpBinding for transport security either in code or
via configuration...In configuration file add a security element to the BasicHttpBinding
element as follows:
<basicHttpBinding>
<binding>
<security mode="None|Transport|Message|TransportWithMessageCredential|TransportCredentialOnly">
<transport
clientCredentialType="None|Basic|Digest|Ntlm|Windows"
proxyCredentialType="None|Basic|Digest|Ntlm|Windows"
realm="string" >
<extendedProtectionPolicy
policyEnforcement="Never|WhenSupported|Always"
protectionScenario="TransportSelected|TrustedProxy">
<customServiceNames></customServiceNames>
</extendedProtectionPolicy>
</transport>
</security>
</binding>
</basicHttpBinding>
Because the binding uses HTTP as underlying
protocol, the request will occur over an SSL-secured connection. In same
way we can configure rest of the available bindings also for more details
please visit MSDN
Courtesy: Random Web Images, Microsoft .NET 3.5 WCF Book, Several online resources
Courtesy: Random Web Images, Microsoft .NET 3.5 WCF Book, Several online resources
No comments:
Post a Comment